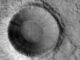
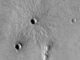
Olivine is a magnesium-iron silicate that is very common on Earth, particularly in the mantle. While the large scale morphology of these craters is well characterized, this is not the case with fine scale layering and fracturing. Understanding these morphologic characteristics in craters could help describe large scale crustal processes on Mars, including the genesis of magmas and the creation of regolith.
There are other regions of Mars that are also rich in olivine. Olivine turns into other minerals in the presence of water, so scientists are interested in looking for those minerals as well.
This caption is based on the original science rationale.